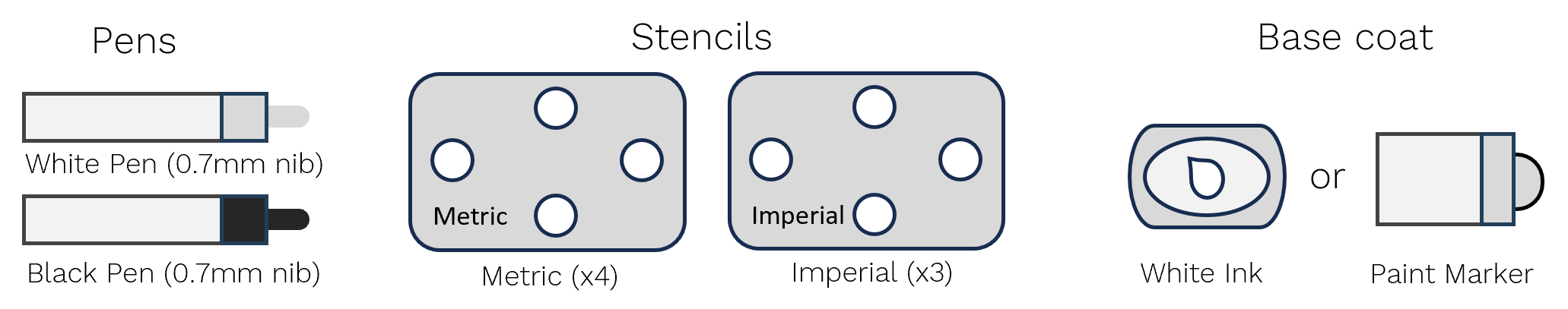
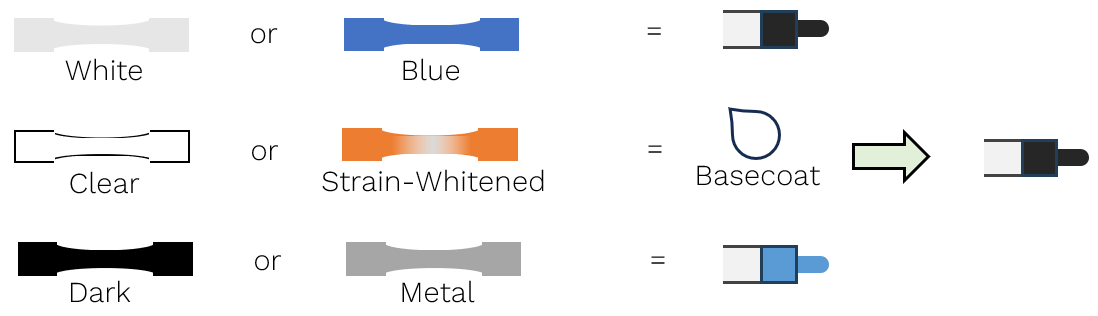
Specimen Marking
Overview
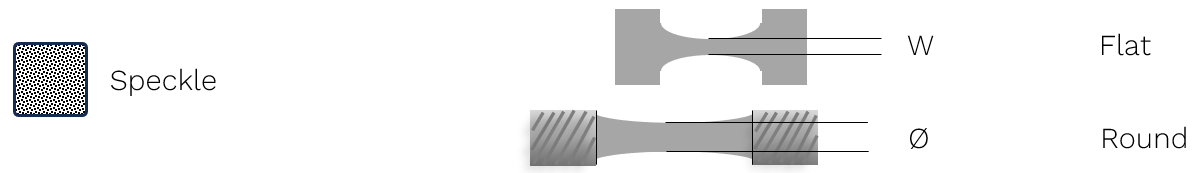
Vector |
Flats Using Rings or Filled Circles |
Flats Using Speckles |
Rounds Using Speckles |
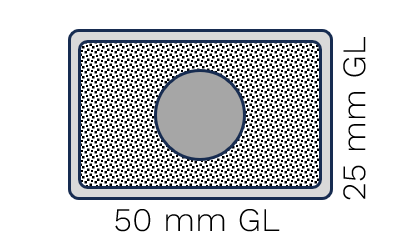
U200 |
W ≥ 8 mm |
W ≥ 5 mm |
Ø ≥ 6 mm |
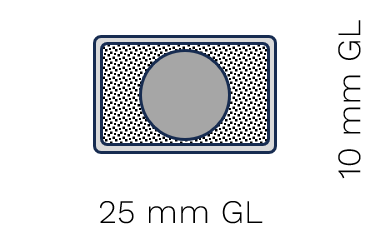
U70 |
W ≥ 4 mm |
W ≥ 2 mm |
Ø ≥ 2.5 mm |
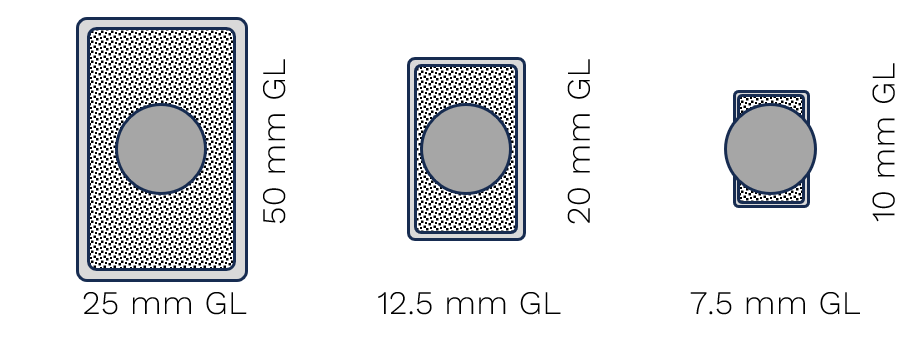
B80 |
W ≥ 4 mm when axial
W ≥ 10 mm when transverse
|
W ≥ 1.5 mm when axial
W ≥ 10 mm when transverse
|
Ø ≥ 2 mm when axial
Ø ≥ 12.5 mm when transverse
|
Warning

Ensure that the correct marking kit is used with each Vector variant
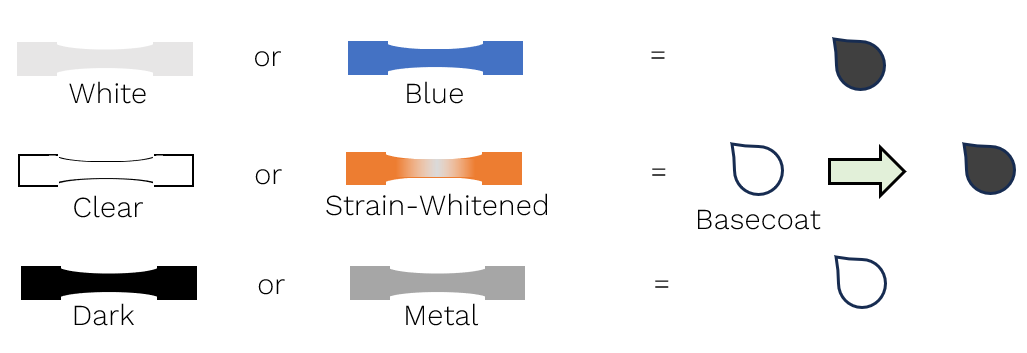
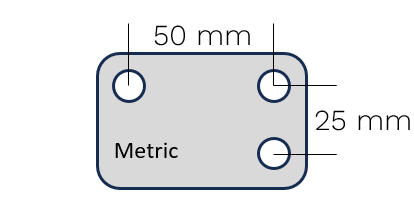
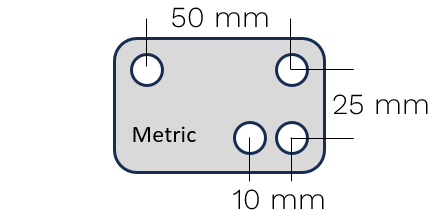
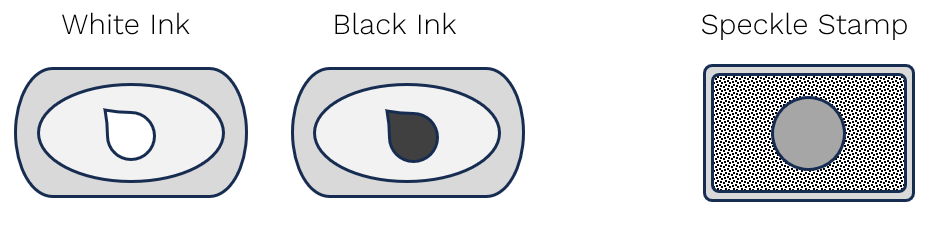
Marking with Rings and Circles
Circles are filled ring markings. The diameter of the ring varies with the Vector variant.
Kit - U200
Kit - U70
Kit - B80
Uses
Vector |
Using Rings or Filled Circles |
U200 |
W ≥ 8 mm |
U70 |
W ≥ 4 mm |
B80 |
W ≥ 4 mm when axial
W ≥ 10 mm when transverse
|
Appearance
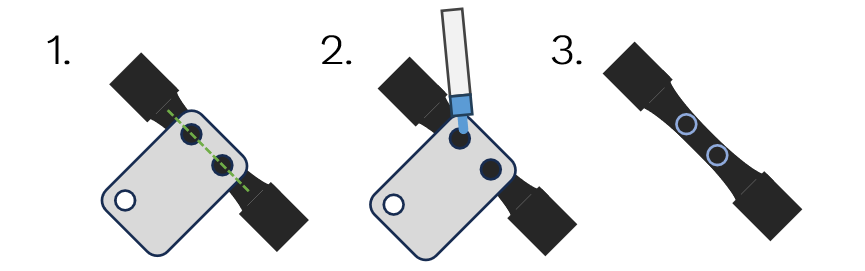
Preparation
Clean specimen to remove grease and dust
Ensure stencil is clean and pen nib is true.
Warning

Do not touch reduced section of specimen once cleaned.
Application
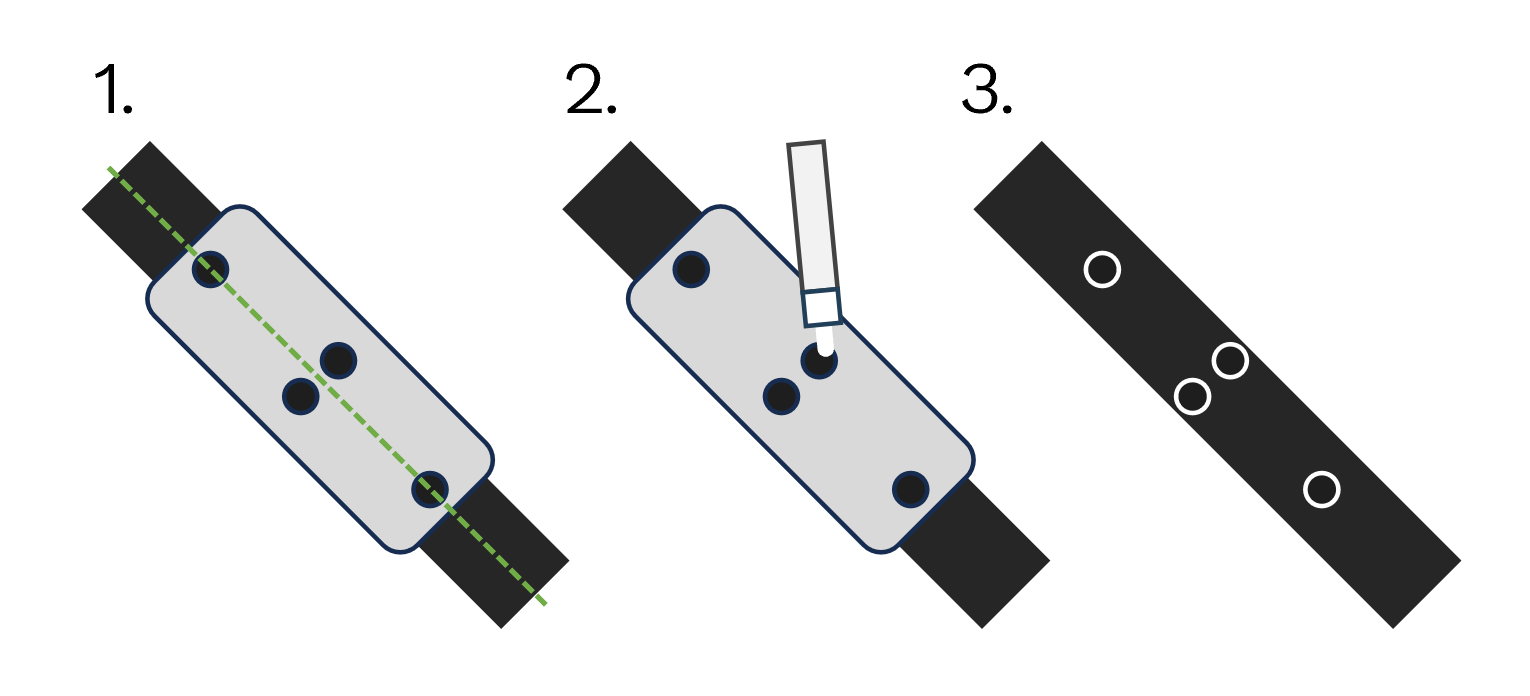
Align stencil to reduced section of specimen.
Evenly draw markings.
- Remove stencil.Take care to avoid smudging the markings.The B80 Combined Stencil works in a similar way.
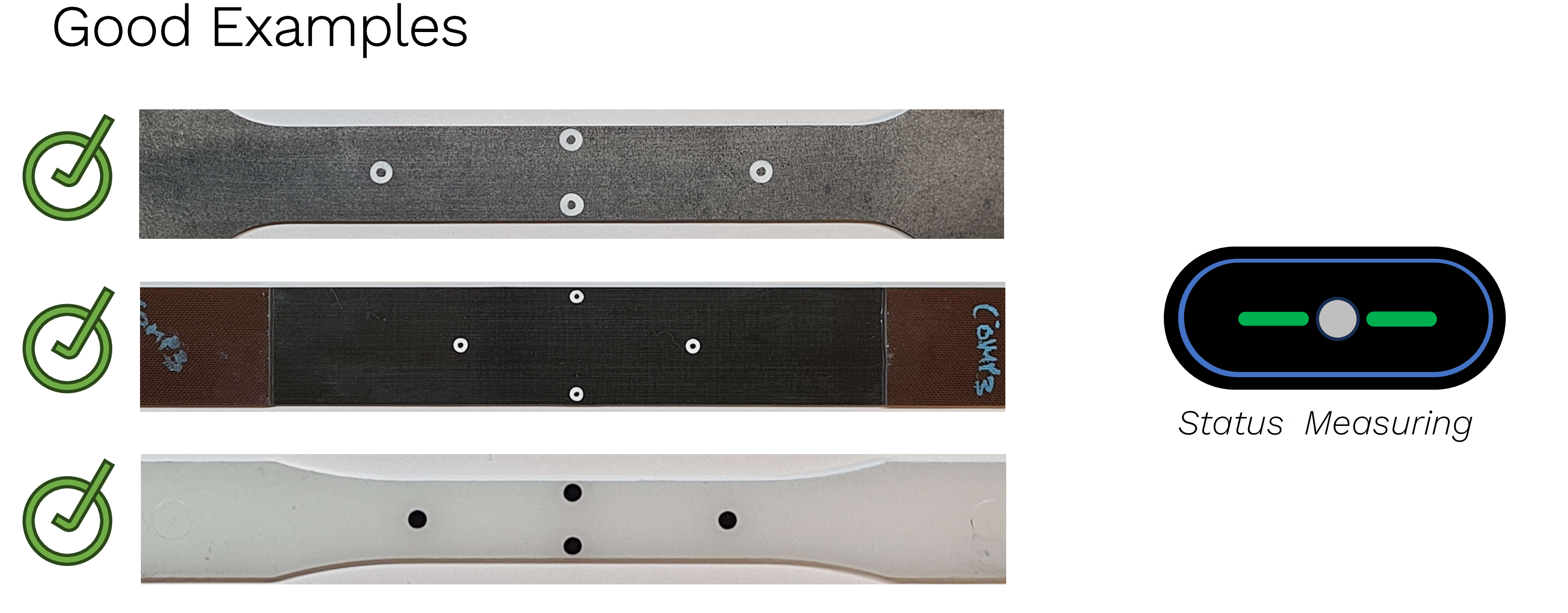
Examples for U200
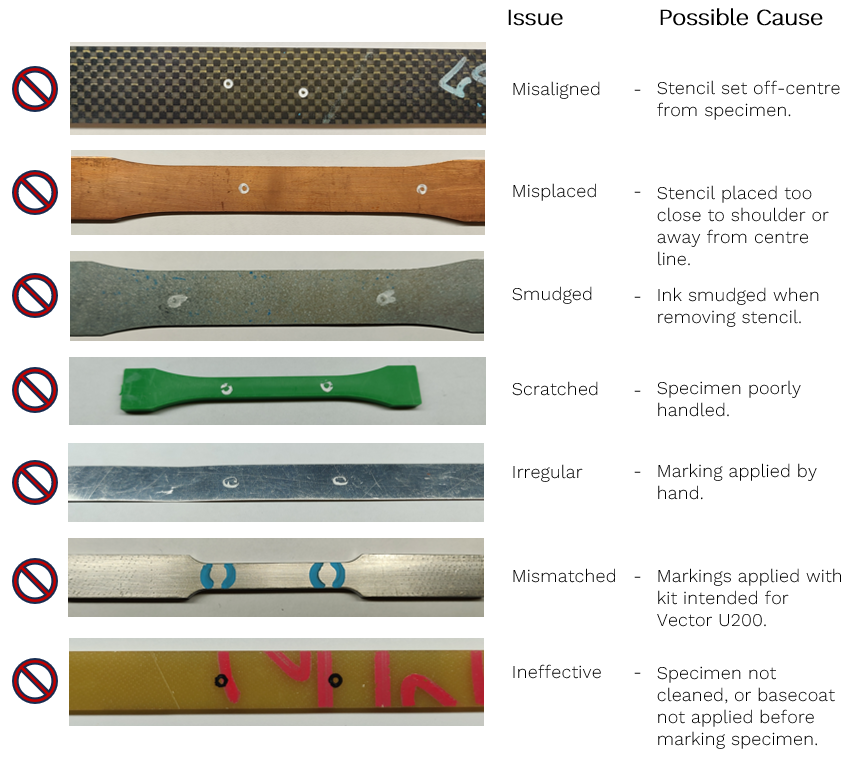
Good Examples
Poor Examples
Examples for U70
Good Examples
Poor Examples
Examples for B80
Good Examples
Poor Examples
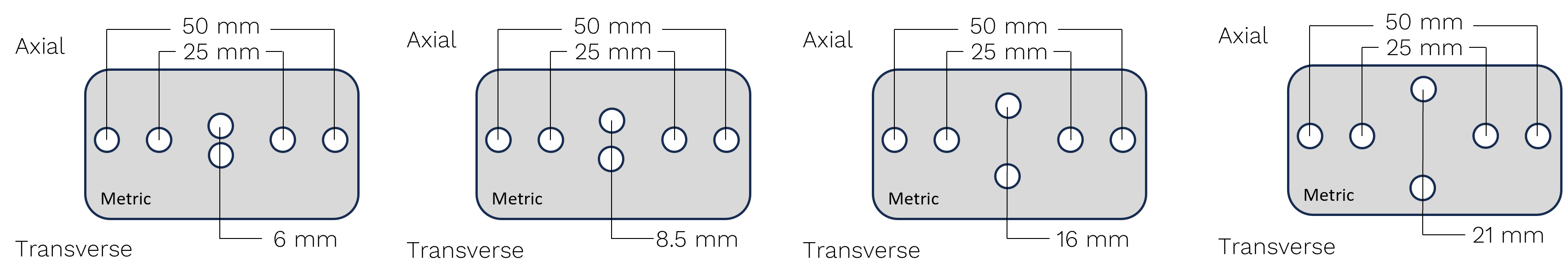
Marking with Speckles
Kit
Uses
Vector |
Flats Using Speckles |
Rounds Using Speckles |
U200 |
W ≥ 5 mm |
Ø ≥ 6 mm |
U70 |
W ≥ 2 mm |
Ø ≥ 2.5 mm |
B80 |
W ≥ 1.5 mm when axial
W ≥ 10 mm when transverse
|
Ø ≥ 2 mm when axial
Ø ≥ 12.5 mm when transverse
|
Appearance
Preparation
Clean specimen to remove grease and dust
Ensure stamp is free from a build-up of ink or debris.
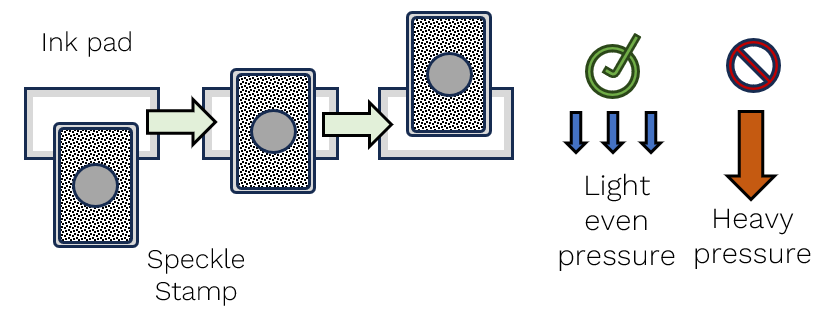
Place stamp on top of ink pad between marking specimens
Information

Warning

Do not touch reduced section of specimen once cleaned.
Application
- Prepare work area.
Place a clean sheet of paper under specimen before stamping.
- Prepare specimen.
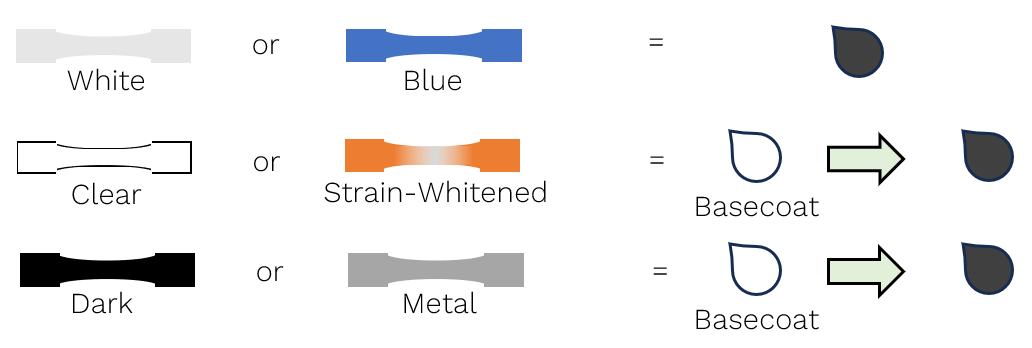
Apply a basecoat, if required, using the contrasting ink.
Select Stamp Orientation for Gauge Length.
- Ink Stamp.
Light even pressure.
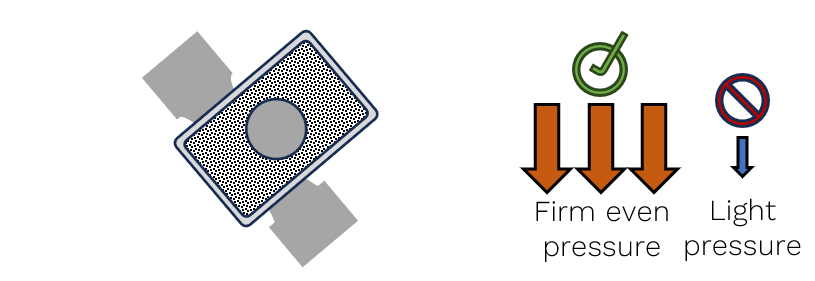
- Apply stamp to specimen.
Firm even pressure.
Information

Allowing for the ink to dry slightly on the stamp before applying will minimise the likelihood of slipping.
Information

A crisp ‘peeling’ sound when removing stamp from specimen is a good indicator that the speckle pattern has been applied effectively.
Warning

Ensure that entire stamp pad is evenly coated in ink.
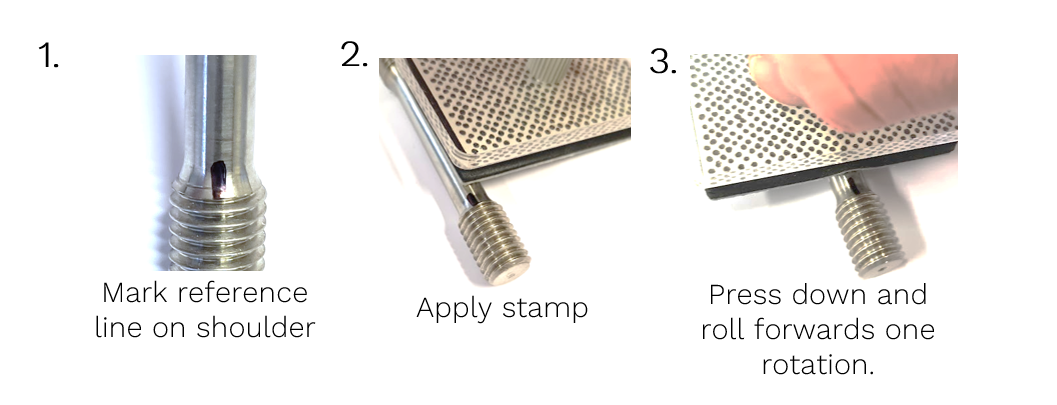
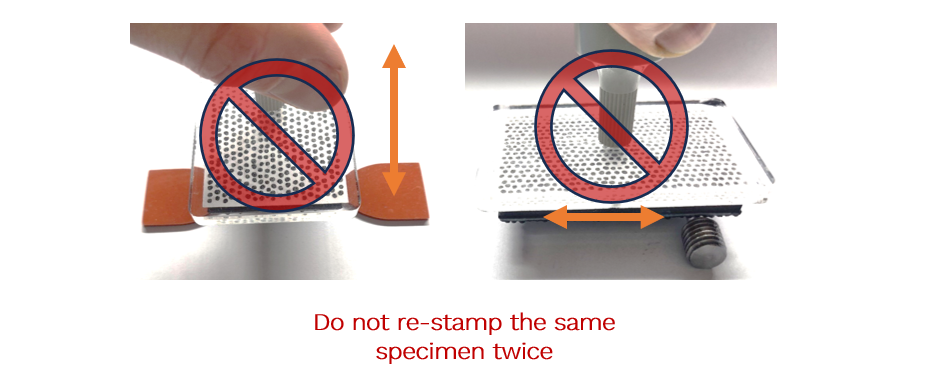
Application Technique
Examples for U200
Poor Examples
Examples for U70
Poor Examples
Examples for B80
Poor Examples